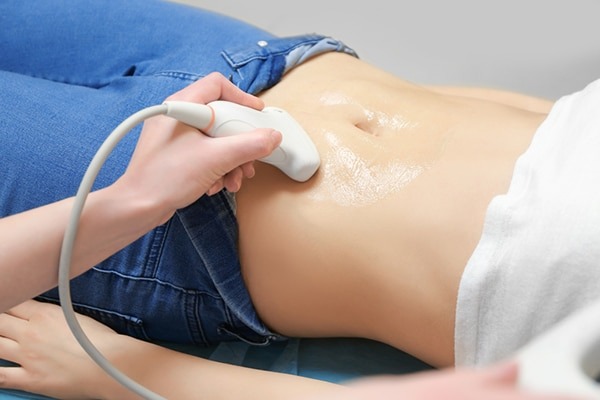
Pelvic Scan
A pelvic scan, also known as a pelvic ultrasound, is a diagnostic imaging procedure used to assess the organs and structures within the pelvis region of the body. It is a non-invasive and painless procedure that utilizes sound waves to create images of the pelvic organs, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder, and prostate gland.
During a pelvic scan, the patient lies on an examination table, and a gel is applied to the skin over the pelvis area to help transmit the sound waves. A transducer, which emits and receives the sound waves, is then moved over the abdomen or inserted into the vagina (transvaginal ultrasound) for better visualization of the pelvic organs.
The images produced during a pelvic scan can help diagnose various conditions and abnormalities, such as ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, and urinary tract disorders. It can also be used to monitor the development of a pregnancy and assess the health of the fetus.
After the pelvic scan is completed, the images are reviewed by a radiologist or healthcare provider to interpret the findings. They will look for any abnormalities or signs of disease and may recommend further testing or treatment based on the results of the scan.
In conclusion, a pelvic scan is a valuable diagnostic tool used to evaluate the health and function of the pelvic organs. It is a safe and effective procedure that provides detailed images to assist in the diagnosis and management of various gynecological, urological, and reproductive conditions.



.png)